Supreme Court Term 2024-2025
Weâre breaking down the cases we've asked the court to consider this term.
Latest Case Updates
Ongoing
Updated June 23, 2025
Ongoing
Updated June 13, 2025
Closed (Judgment)
Updated June 6, 2025
Ongoing
Updated May 8, 2025
Featured
Georgia Supreme Court
Jun 2025

Voting Rights
Eternal Vigilance Action, Inc. v. Georgia
The ĖĮÐÄVlogand partner organizations intervened in this case to represent the rights of voters and voting-rights organizations in a case challenging a number of rules passed by the Georgia State Election Board. We challenged the rule requiring that the number of votes cast be hand counted at the polling place prior to the tabulation of votes. In a critical victory for Georgia voters, in June 2025, the Georgia Supreme Court upheld a lower courtâs decision permanently blocking the rule requiring hand counting of ballots at polling places before tabulation â a process widely criticized for risking delays, ballot spoliation, and voter disenfranchisement.
U.S. Supreme Court
May 2025
Voting Rights
Racial Justice
Allen v. Milligan
Whether Alabamaâs congressional districts violate Section 2 of the Voting Rights Act because they discriminate against Black voters. We succeeded in winning a new map for 2024 elections which, for the first time, has two congressional district that provide Black voters a fair opportunity to elect candidates of their choosing despite multiple attempts by Alabama to stop us at the Supreme Court. Despite this win, Alabama is still defending its discriminatory map, and a trial was held in February 2025 to determine the map for the rest of the decade.
In May 2025, a federal court ruled that Alabama's 2023 congressional map both violates Section 2 of the Voting Rights Act and was enacted by the Alabama Legislature with racially discriminatory intent.
Washington, D.C.
Apr 2025

Voting Rights
League of Women Voters Education Fund v. Trump
On March 25, 2025, in a sweeping and unprecedented Executive Order, President Trump attempted to usurp the power to regulate federal elections from Congress and the States. Among other things, the Executive Order directs the Election Assistance Commissionâan agency that Congress specifically established to be bipartisan and independentâto require voters to show a passport or other citizenship documentation in order to register to vote in federal elections. If implemented, the Executive Order would threaten the ability of millions of eligible Americans to register and vote and upend the administration of federal elections.
On behalf of leading voter registration organizations and advocacy organizations, the ĖĮÐÄVlogand co-counsel filed a lawsuit to block the Executive Order as an unconstitutional power grab.
Maryland
Apr 2025

Religious Liberty
LGBTQ Rights
Mahmoud v. Taylor
On April 9, 2025, the ĖĮÐÄVlogand ĖĮÐÄVlogof Maryland filed an amicus brief with the U.S. Supreme Court supporting the Montgomery County Public Schools (MCPS) in its efforts to ensure that its English Language Arts curriculum is LGBTQ-inclusive.
U.S. Supreme Court
Mar 2025
Voting Rights
Callais v. Landry
Whether the congressional map Louisiana adopted to cure a Voting Rights Act violation in Robinson v. Ardoin is itself unlawful as a gerrymander.
New Hampshire
Mar 2025

Voting Rights
Coalition for Open Democracy v. Scanlan
This lawsuit challenges HB 1569, a new law that will make New Hampshire the only state to require every person to produce documentary proof of citizenship when they register to vote for both state and federal elections. It also challenges HB 1569âs elimination a preexisting protection for votersânamely, an affidavit option that allowed voters who faced surprise challenges to their eligibility at the polls to swear to their qualifications and cast a ballot. Accordingly, HB 1569 violates the First and Fourteenth Amendments of the U.S. Constitution by placing substantial burdens on New Hampshirites at all stages of the voting process, and will arbitrarily disenfranchise hundreds, if not thousands of qualified voters.
South Carolina Supreme Court
Jan 2025

Voting Rights
League of Women Voters of South Carolina v. Alexander
This case involves a state constitutional challenge to South Carolinaâs 2022 congressional redistricting plan, which legislators admit was drawn to entrench a 6-1 Republican majority in the stateâs federal delegation. Plaintiff the League of Women Voters of South Carolina has asked the stateâs Supreme Court to conclude that the congressional map is an unlawful partisan gerrymander that violates the state constitution.
Texas
Oct 2024

Voting Rights
OCA-Greater Houston v. Paxton
Texas has growing Hispanic and Black populations that helped propel record voter turnout in the November 2020 election. The Texas Legislature responded to this increased civic participation with an omnibus election bill titled Senate Bill 1âSB 1 for shortâthat targeted election practices that made voting more accessible to traditionally marginalized voters like voters of color, voters with disabilities, and voters with limited English proficiency. Since 2021, SB 1 has resulted in tens of thousands of lawful votes being rejected, and it remains a threat to democracy in Texas.
Ohio
Sep 2024

Reproductive Freedom
Planned Parenthood Southwest Ohio Region et al., v. Ohio Department of Health, et al.
The ĖĮÐÄVlog, the ĖĮÐÄVlogof Ohio, Planned Parenthood Federation of America, the law firm WilmerHale, and Fanon Rucker of the Cochran Law Firm, on behalf of Planned Parenthood Southwest Ohio Region, Planned Parenthood of Greater Ohio, Preterm-Cleveland, Womenâs Med Group Professional Corporation, Dr. Sharon Liner, and Julia Quinn, MSN, BSN, amended a complaint in an existing lawsuit against a ban on telehealth medication abortion services to bring new claims under the Ohio Reproductive Freedom Amendment, including additional challenges to other laws in Ohio that restrict access to medication abortion in the state.
All Cases
1,586 Court Cases

Court Case
Feb 2023
Free Speech
C.K.âW. v. Wentzville R-IV School District
The ĖĮÐÄVlog of Missouri, joined by the National ACLU, filed a lawsuit challenging a school district's removal of eight critically-acclaimed library books that are by and about people of color, LGBTQ+ people, and other marginalized groups, as well as its policy requiring automatic removal of every book that any student, parent, or guardian formally objects to, regardless of the basis for or merits of that objection.
Explore case
Court Case
Feb 2023

Free Speech
C.K.âW. v. Wentzville R-IV School District
The ĖĮÐÄVlog of Missouri, joined by the National ACLU, filed a lawsuit challenging a school district's removal of eight critically-acclaimed library books that are by and about people of color, LGBTQ+ people, and other marginalized groups, as well as its policy requiring automatic removal of every book that any student, parent, or guardian formally objects to, regardless of the basis for or merits of that objection.

Virginia
Feb 2023
LGBTQ Rights
+2 ĖĮÐÄVlog
Vlaming v. West Point School District
In September of 2019, Peter Vlaming, a French teacher at West Point High School, refused to address a transgender boy in his class with he/him pronouns. Instead, the teacher avoided using pronouns when addressing the student, while continuing to use gendered pronouns when addressing everyone else. After several warnings, the school district told the teacher he needed to address the student with male pronouns (the same way he addressed other boys) or he would be fired. The teacher refused; the school district fired him, and Vlaming, represented by the Alliance Defending Freedom, filed a suit in state court arguing that the school district violated his free speech and free exercise rights under the Virginia Constitution and Virginiaâs RFRA.
Explore case
Virginia
Feb 2023

LGBTQ Rights
+2 ĖĮÐÄVlog
Vlaming v. West Point School District
In September of 2019, Peter Vlaming, a French teacher at West Point High School, refused to address a transgender boy in his class with he/him pronouns. Instead, the teacher avoided using pronouns when addressing the student, while continuing to use gendered pronouns when addressing everyone else. After several warnings, the school district told the teacher he needed to address the student with male pronouns (the same way he addressed other boys) or he would be fired. The teacher refused; the school district fired him, and Vlaming, represented by the Alliance Defending Freedom, filed a suit in state court arguing that the school district violated his free speech and free exercise rights under the Virginia Constitution and Virginiaâs RFRA.

South Carolina
Feb 2023
Juvenile Justice
+2 ĖĮÐÄVlog
CYAP v. Wilson
The ĖĮÐÄVlog filed a federal lawsuit challenging South Carolinaâs âdisturbing schoolsâ and âdisorderly conductâ laws. The laws allowed students in school to be criminally charged for normal adolescent behaviors including loitering, cursing, or undefined âobnoxiousâ actions on school grounds and encouraged discriminatory enforcement against Black students and students with disabilities. The Fourth Circuit Court of Appeals affirmed the district court ruling that enforcing these laws against students was unconstitutional, affirming that subjecting students to criminal penalties under such vague rules interferes with their education and their future, and produces stark racial disparities. This decision should be instructive to the many school districts across the country where students continue to be charged with âdisorderly conductâ and similar vague crimes.
Explore case
South Carolina
Feb 2023

Juvenile Justice
+2 ĖĮÐÄVlog
CYAP v. Wilson
The ĖĮÐÄVlog filed a federal lawsuit challenging South Carolinaâs âdisturbing schoolsâ and âdisorderly conductâ laws. The laws allowed students in school to be criminally charged for normal adolescent behaviors including loitering, cursing, or undefined âobnoxiousâ actions on school grounds and encouraged discriminatory enforcement against Black students and students with disabilities. The Fourth Circuit Court of Appeals affirmed the district court ruling that enforcing these laws against students was unconstitutional, affirming that subjecting students to criminal penalties under such vague rules interferes with their education and their future, and produces stark racial disparities. This decision should be instructive to the many school districts across the country where students continue to be charged with âdisorderly conductâ and similar vague crimes.
U.S. Supreme Court
Feb 2023
National Security
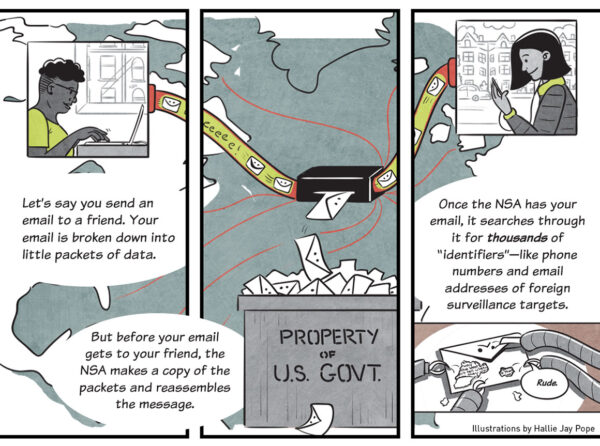
Wikimedia v. NSA - Challenge to Upstream Surveillance
The ĖĮÐÄVlogis challenging the constitutionality of the NSAâs mass interception and searching of Americansâ international Internet communications. At issue is the NSAâs âUpstreamâ surveillance, through which the U.S. government systematically monitors private emails, messages, and other data flowing into and out of the country on the Internetâs central arteries. The ACLUâs lawsuit was brought on behalf of the Wikimedia Foundation and eight legal, human rights, and media organizations, which together engage in trillions of sensitive communications and have been harmed by Upstream surveillance.
Explore case
U.S. Supreme Court
Feb 2023

National Security
Wikimedia v. NSA - Challenge to Upstream Surveillance
The ĖĮÐÄVlogis challenging the constitutionality of the NSAâs mass interception and searching of Americansâ international Internet communications. At issue is the NSAâs âUpstreamâ surveillance, through which the U.S. government systematically monitors private emails, messages, and other data flowing into and out of the country on the Internetâs central arteries. The ACLUâs lawsuit was brought on behalf of the Wikimedia Foundation and eight legal, human rights, and media organizations, which together engage in trillions of sensitive communications and have been harmed by Upstream surveillance.

U.S. Supreme Court
Feb 2023
Free Speech
Civil Liberties
United States v. Helaman Hansen
This case is about whether the First Amendment permits criminal punishment of speech that merely encourages a noncitizen to remain in the United States, without any requirement of intent to further illegal conduct, and when remaining in the United States unlawfully is itself not a crime.
Explore case
U.S. Supreme Court
Feb 2023

Free Speech
Civil Liberties
United States v. Helaman Hansen
This case is about whether the First Amendment permits criminal punishment of speech that merely encourages a noncitizen to remain in the United States, without any requirement of intent to further illegal conduct, and when remaining in the United States unlawfully is itself not a crime.